























No part of this publication may be reproduced, or transmitted, or stored, in any form or
by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without
the prior written permission of SheetMetalWorkBook.com
Sixth Edition Reformatted for Internet
©2012 SheetMetalWorkBook.com





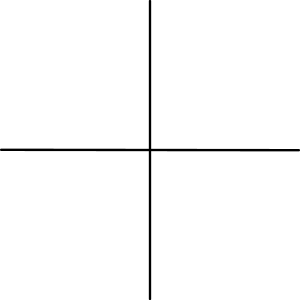
Coordinate Systems
CARTESIAN COORDINATES:
EITHER ONE OR TWO INTERSECTING
LINES WHICH DETERMINE THE POSITION
OF EVERY POINT IN A PLANE. X & Y
IDENTIFY THE AXIS. X IS NORMALLY
HORIZONTAL AND Y IS VERTICAL.
(ALSO CALLED RECTANGULAR
COORDINATES.
1 2 3 4 5
-5 -4 -3 -2 -1
5
4
3
2
1
-1
-2
-3
-4
-5
2 DIMENSIONAL OR 2 AXIS
(FLAT PLANE)
(Y AXIS)
(X AXIS)
(2,1)
(3,2.5)
(4,3)
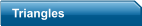
ORIGIN IS 0,0
X DIMENSION IS FIRST
WHEN DEFINING POINTS
IF YOU MIRROR THESE POINTS
AROUND THE Y AXIS THEN THE
VALUE OF X IS CHANGED TO
NEGATIVE NUMBERS
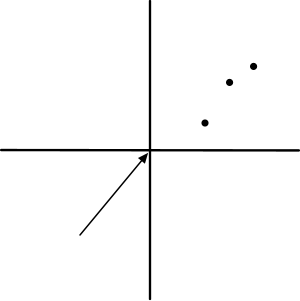
3 DIMENSIONAL OR 3 AXIS (COORDINATES IN SPACE)
(Y AXIS)
(X AXIS)
(Z AXIS)
ORIGIN IS 0,0
3
2
1
-1
-2
-3
-3 -2 -1
1 2 3
3
2
1
-1
-2
-3
YOU COULD DETERMINE
THE RECTANGULAR
COORDINATES FROM
POLAR COORDINATES BY
USING TRIGONOMETRY TO
WORK OUT THE PROBLEM.
WHERE AN ANGLE &
DISTANCE (RADIUS)
DETERMINES THE
POSITION OF A POINT
sin(30) x 1.500 = Y VALUE
cos(30) x 1.500 = X VALUE
POLAR COORDINATE
(Y AXIS)
(X AXIS)

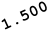


30°